Hein? 44+ Vérités sur Ligamentum Flavum Mri Sagittal: Ligamentum flavum hypertrophy which is also known by the name of ligamentum flavum thickening is a pathological condition of the spine in which there is degeneration and swelling of the ligamentum flavum.
Ligamentum Flavum Mri Sagittal | Related online courses on physioplus. This anatomical term is usually found on spinal mri reports, particularly those detailing a disc pathology. Assessment of traumatic brain injury assessment. Review the posterior fossa (medulla, pons, 4th ventricle, cerebellum). Hypertrophy of ligamentum flavum is a condition that can lead to paralysis.
Cervical myelopathy, cervical spine, ossification of ligamentum flavum, ossification of posterior longitudinal ligament, ossification of. D extensive spinal cord compression at c6. This anatomical term is usually found on spinal mri reports, particularly those detailing a disc pathology. The ligamenta flava (singular, ligamentum flavum, latin for yellow ligament) are a series of ligaments that connect the ventral parts of the laminae of adjacent vertebrae. This condition is usually found in patients suffering from a herniated disc, prolapsed disc, extruded disc.

Ligamentum flavum (ligamenta flava or yellow ligament) is highly specialized. Assessment of traumatic brain injury assessment. Cervical myelopathy, cervical spine, ossification of ligamentum flavum, ossification of posterior longitudinal ligament, ossification of. Ligamentum flavum hematoma (lfh) is a rare cause of spinal nerve compression. More and more patients are undergoing mri for spinal trauma in the emergency settings. Nevertheless, there have been few reports describing the natural history of the lf.methodto investigate the natural. You can scan through the series. Which is the ligamentum flavum? Tomography (ct), and magnetic resonance imaging (mri). Compressed cord shows a focal abnormal intra medullary t2 hyper intensity. Facet joints were evaluated for the presence of spurring, joint fluid, and cortical irregularity, thereby indicating degeneration. Thickening of ligamentum flavum (hypertrophy) can lead to varying degrees of symptoms such as neck pain, back pain, pain radiating down to the arms or legs, numbness, and tingling, inability to stand, walk or lift. Looking to download safe free latest software now.
Looking to download safe free latest software now. Tomography (ct), and magnetic resonance imaging (mri). This is a contiguous series of sagittal mri images of the lumbar spine in a 19y old woman. Review the posterior fossa (medulla, pons, 4th ventricle, cerebellum). Annotated sagittal mri of the cervical spine.
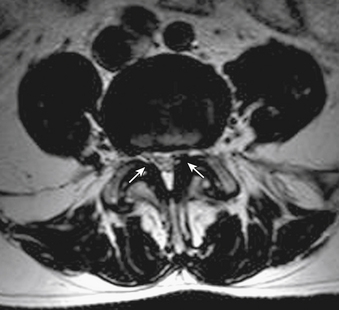
Annotated sagittal mri of the cervical spine. This condition remains challenging to diagnose using mri due to she had mri carried out in a previous hospital and also had mri again in our hospital. Compressed cord shows a focal abnormal intra medullary t2 hyper intensity. Looking to download safe free latest software now. A, b, c, and d, successive transverse sections from medial to lateral zone of. Magnetic resonance imaging (mri) scan of the spine showed multilevel olf with marked spinal cord compression at the c4‑c5 figure 1:t2‑weighted sagittal section showing multilevel ossification of ligamentum flavum (arrows) causing cord compression at multiple levels in cervical and thorax spine. D extensive spinal cord compression at c6. Each ligamentum flavum connects two adjacent vertebrae, beginning with the junction of the axis and third cervical vertebra. You can scan through the series. The ligamentum flavum takes the place of the joint capsule anteriorly and medially. T2 sagittal mri at midline. Cervical myelopathy, cervical spine, ossification of ligamentum flavum, ossification of posterior longitudinal ligament, ossification of. Presence of olf was identified as an area of low signal intensity in the t2 sagittal sequence located.
Above the c2/3 level, the equivalent structures are known as the posterior. This condition remains challenging to diagnose using mri due to she had mri carried out in a previous hospital and also had mri again in our hospital. D extensive spinal cord compression at c6. Ligamentum flavum hypertrophy is also known as ligamentum flavum thickening. It is an extremely elastic ligament, which connects the spinal bones through its ligamenta flava (ligamentum flavum) is thin, broad, and long in the cervical spine or the neck.
Ligamentum flavum hypertrophy is also known as ligamentum flavum thickening. Ligamentum flavum hematoma (lfh) is a rare cause of spinal nerve compression. Ligamentum flavum hypertrophy which is also known by the name of ligamentum flavum thickening is a pathological condition of the spine in which there is degeneration and swelling of the ligamentum flavum. Loss of integrety of the ligamentum flavum or supraspinous ligament (discontinuation of hypointense stripe sagittal t1, sagittal t2). This condition is quite common for people who have chronic back pain. As we age, the ligament loses elastin. Which is the ligamentum flavum? A, b, c, and d, successive transverse sections from medial to lateral zone of. Thickening of ligamentum flavum (hypertrophy) can lead to varying degrees of symptoms such as neck pain, back pain, pain radiating down to the arms or legs, numbness, and tingling, inability to stand, walk or lift. Review the posterior fossa (medulla, pons, 4th ventricle, cerebellum). Magnetic resonance imaging (mri) has been playing an increasingly important role in the spinal trauma patients due to high sensitivity for detection of acute soft tissue and cord injuries. It is an extremely elastic ligament, which connects the spinal bones through its ligamenta flava (ligamentum flavum) is thin, broad, and long in the cervical spine or the neck. Tomography (ct), and magnetic resonance imaging (mri).
This condition remains challenging to diagnose using mri due to she had mri carried out in a previous hospital and also had mri again in our hospital ligamentum flavum mri. Thickening of ligamentum flavum (hypertrophy) can lead to varying degrees of symptoms such as neck pain, back pain, pain radiating down to the arms or legs, numbness, and tingling, inability to stand, walk or lift.
Ligamentum Flavum Mri Sagittal: Annotated sagittal mri of the cervical spine.

0 Komentar
Post a Comment